转贴一个讲孪晶的网页,来自Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson
cuturl('http://www.tulane.edu/~sanelson/eens211/twinning.htm')
Twinning in Crystals
Sometimes during the growth of a crystal, or if the crystal is subjected to stress or temperature/pressure conditions different from those under which it originally formed, two or more intergrown crystals are formed in a symmetrical fashion. These symmetrical intergrowths of crystals are called twinned crystals. Twinning is important to recognize, because when it occurs, it is often one of the most diagnostic features enabling identification of the mineral.
What happens is that lattice points in one crystal are shared as lattice points in another crystal adding apparent symmetry to the crystal pairs. Twinning, because it adds symmetry, never occurs in relation to the existing symmetry of the crystal.
Symmetry Operations that Define Twinning
Because symmetry is added to a crystal by twinning, twining can be defined by the symmetry operations that are involved. These include:
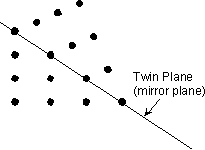
。Reflection across a mirror plane. The added mirror plane would then be called a twin plane.
。Rotation about an axis or line in the crystal. The added rotation axis would then be called a twin axis.
。Inversion through a point. The added center of symmetry would then be called a twin center.
Twin Laws
Twin laws are expressed as either form symbols to define twin planes (i.e. {hkl}) or zone symbols to define the direction of twin axes (i.e. [hkl]).
The surface along which the lattice points are shared in twinned crystals is called a composition surface.
If the twin law can be defined by a simple planar composition surface, the twin plane is always parallel to a possible crystal face and never parallel to an existing plane of symmetry (remember that twinning adds symmetry).
If the twin law is a rotation axis, the composition surface will be irregular, the twin axis will be perpendicular to a lattice plane, but will never be an even-fold rotation axis of the existing symmetry. For example twinning cannot occur on a new 2 fold axis that is parallel to an existing 4-fold axis.
Types of Twinning
Another way of defining twinning breaks twins into two separate types.
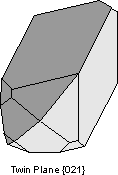
1. Contact Twins - have a planar composition surface separating 2 individual crystals. These are usually defined by a twin law that expresses a twin plane (i.e. an added mirror plane). An example shown here is a crystal of orthoclase twinned on the Braveno Law, with {021} as the twin plane.